Setup
① Add app to INSTALLED_APPS
# project/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
"signal_webhooks",
...
]
② Run migrations
python manage.py migrate
You should now see the webhooks section in django's admin panel.
③ Define webhook settings
The easiest way to add webhooks is just to use the default configuration by settings ... (ellipses) to a model in the HOOKS configuration option.
# project/settings.py
SIGNAL_WEBHOOKS = {
"HOOKS": {
# Add default webhook configuration to the User model
"django.contrib.auth.models.User": ...,
},
}
This will allow webhooks to be fired for the User model. You can also set the value to a string in dot import notation, pointing to a custom function, or to None to explicitly forbid hooks for a given model. You can also set these for each signal separately.
# project/settings.py
SIGNAL_WEBHOOKS = {
"HOOKS": {
"django.contrib.auth.models.User": {
"CREATE": None,
"UPDATE": "my.custom.func",
"DELETE": ...,
# Many to many post signals
"M2M_ADD": ...,
"M2M_REMOVE": ...,
"M2M_CLEAR": ...,
},
},
}
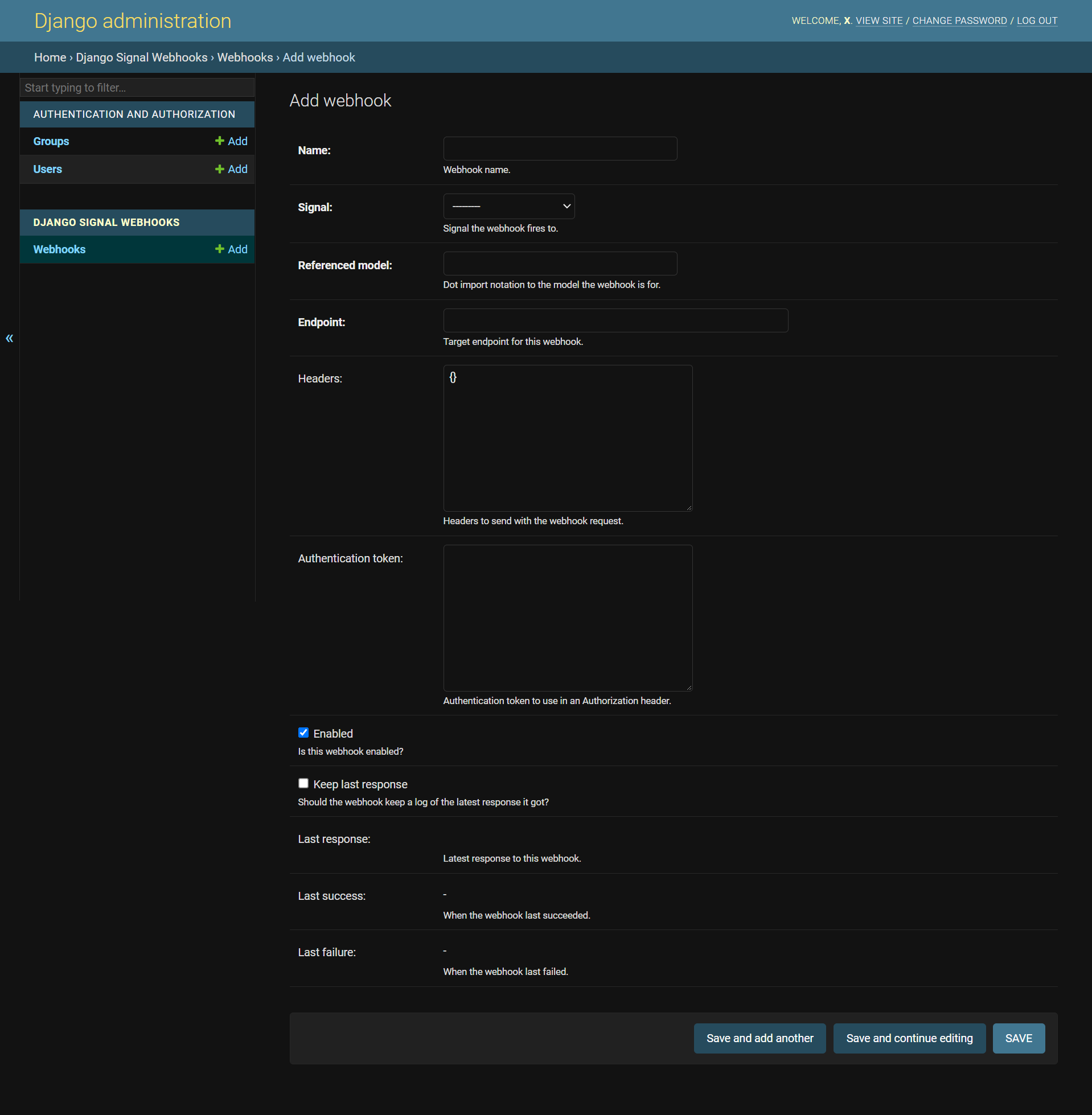
④ Add hooks in the admin panel
You must give each webhook a unique name, the signals it listens to,
the references model (in dot import notation), and the endpoint
it will call. You can also set any headers you want, as well as
an authentication token that will be used in the Authorization
header in the webhook. This token will be ciphered using
SIGNAL_WEBHOOKS.CIPHER_KEY when saved to the database to
prevent it from being stolen. Ticking the keep_last_reponse
checkbox will allow webhook responses to be recorded in the
last_reponse field.
⑤ That's it!
Webhooks should now be fired for the defined signals. Here is an example of what the default configuration will send for the User model.
{
"model": "auth.user",
"pk": 1,
"fields": {
"password": "pbkdf2_sha256$390000$79U11eoHYvz4v33cXo5373$bNN8Q0NpvOowd1od9pBUNG1WJ4zUIz4eOlaSOQNbop8=",
"last_login": null,
"is_superuser": false,
"username": "foo",
"first_name": "",
"last_name": "",
"email": "",
"is_staff": false,
"is_active": true,
"date_joined": "2022-08-21 20:37:38.714905+00:00",
"groups": [],
"user_permissions": []
}
}
You can set different data for these requests in various ways,
like with SIGNAL_WEBHOOKS.SERIALIZER setting, or on per-model
basis by defining a webhook_data method on the model.
Have a look at the available settings.